Journey through the key milestones and developments of Singapore's energy sector.
Singapore's first electric street lights are switched on.
Singapore’s first coal-fired power plant, St James Power Station, officially opens.
Singapore's first traffic lights flicker on at Empress Place.
Singapore’s first air-conditioned cinema, Cathay Cinema, opens its doors to the public.

(1939) Singapore’s first air-conditioned cinema
Singapore begins the Rural Electrification Programme, which allows rural homes in Singapore to receive electricity from the national power grid.
Pasir Panjang Power Station, which opened in 1953, is expanded in light of our rapid industrialisation.

(Photo courtesy of National Archives of Singapore)
Stricter electrical safety regulations are implemented in the wake of the Robinsons Department Store electrical fire at Raffles Place. These include requiring all elevators be able to return to the ground floor in the event of a fire, and activating standby generators within five minutes of any power failure to power essential and critical equipment.
Ulu Pandan Incinerator becomes Singapore’s first incinerator plant to generate electricity using waste.
Pulau Seraya becomes Singapore’s first offshore power plant with three 250 MW generating steam plants.
Singapore starts importing natural gas from Malaysia.
The Energy Market Authority (EMA) is established to ensure a reliable and secure energy supply, promote effective competition in the energy market, and develop a dynamic energy sector in Singapore.
Singapore starts importing natural gas from Indonesia.
A micro-grid is launched in Pulau Ubin, incorporating solar photovoltaic technology to provide residents with lower costs, and a cleaner and more reliable electricity supply.
The Open Electricity Market is launched to allow household consumers more choices and flexibility when buying electricity.

Open Electricity Market
A nationwide rollout of advanced electricity meters is announced, empowering households to use energy more efficiently.
Singapore announces its electricity imports trial of 100 MW from Malaysia.
Singapore unveils its whole-of-nation agenda for sustainable development (Singapore Green Plan 2030).
Singapore announces its plan to import up to 4 GW of low-carbon electricity by 2035, starting with trials like the Lao PDR-Thailand-Malaysia-Singapore Power Integration Project (LTMS-PIP).
Singapore commences import of 100 MW of hydropower from Lao PDR, as part of the LTMS-PIP.
Singapore unveils its National Hydrogen Strategy at the Singapore International Energy Week 2022.
Southeast Asia's largest Energy Storage System (ESS) opens in Singapore.
The ESS is an integrated system comprising more than 800 large-scale battery units and includes liquid cooling systems or built-in air conditioning systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures (Photo courtesy of Sembcorp Industries)
EMA grants its first Conditional Approval to Keppel Energy Pte Ltd to import 1 GW of electricity from Cambodia into Singapore.
EMA's subsidiary, Meranti Power announces its plan to build two 340 MW Open Cycle Gas Turbine units.

Artist impression of Meranti Power's Open Cycle Gas Turbine generating units in Jurong Island
In Jun, EMA enhances its Energy Management System (EMS) with advanced tools and capabilities to better monitor and control Singapore’s electricity and natural gas transmission networks.
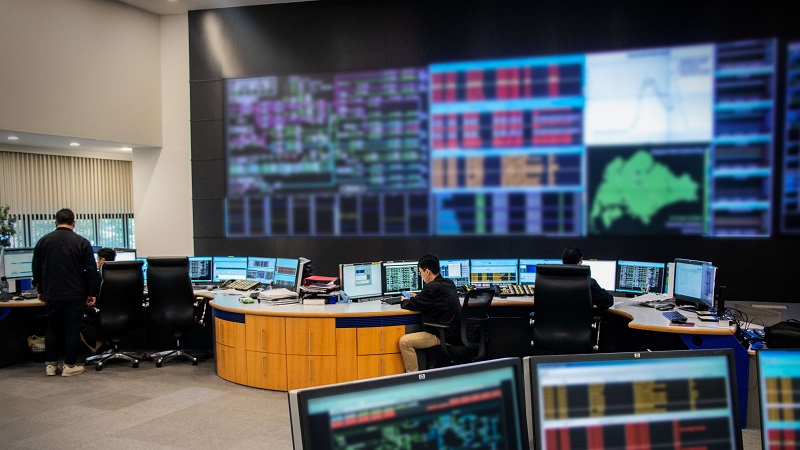

EMS: A real-time mission-critical operational technology system that detects any abnormal condition or malfunction of equipment in the power and gas systems.